How To Find Natural Log Of A Number
Natural Logarithm - ln(x)
Natural logarithm is the logarithm to the base e of a number.
- Natural logarithm (ln) definition
- Natural logarithm (ln) rules & properties
- Derivative of natural logarithm (ln)
- Integral of natural logarithm (ln)
- Complex logarithm
- Graph of ln(x)
- Natural logarithms (ln) tabular array
- Natural logarithm estimator
Definition of natural logarithm
When
e y = x
And so base of operations e logarithm of x is
ln(x) = log east (x) = y
The e constant or Euler's number is:
e ≈ ii.71828183
Ln as inverse part of exponential function
The natural logarithm function ln(x) is the inverse part of the exponential role ex.
For ten>0,
f (f -1(x)) = e ln(x) = ten
Or
f -one(f (x)) = ln(eastx ) = x
Natural logarithm rules and properties
| Rule name | Rule | Instance |
|---|---|---|
Product rule | ln(10 ∙ y) = ln(10) + ln(y) | ln(3 ∙ vii) = ln(3) + ln(7) |
Quotient rule | ln(x / y) = ln(x) - ln(y) | ln(3 / 7) = ln(iii) - ln(vii) |
Power rule | ln(10 y ) = y ∙ ln(ten) | ln(2 eight ) = 8∙ ln(ii) |
ln derivative | f (x) = ln(10) ⇒ f ' (ten) = 1 / x | |
ln integral | ∫ ln(x)dx = x ∙ (ln(ten) - 1) + C | |
ln of negative number | ln(x) is undefined when x ≤ 0 | |
ln of nada | ln(0) is undefined | |
| | ||
ln of one | ln(1) = 0 | |
ln of infinity | lim ln(x) = ∞ ,when x→∞ | |
| Euler's identity | ln(-ane) = iπ |
Logarithm product dominion
The logarithm of the multiplication of x and y is the sum of logarithm of x and logarithm of y.
log b (x ∙ y) = log b (10) + log b (y)
For example:
log10(iii ∙ vii) = log10(3) + log10(7)
Logarithm quotient rule
The logarithm of the partition of ten and y is the difference of logarithm of x and logarithm of y.
log b (x / y) = log b (10) - log b (y)
For example:
log10(3 / 7) = logx(iii) - log10(7)
Logarithm ability rule
The logarithm of ten raised to the ability of y is y times the logarithm of x.
log b (x y ) = y ∙ log b (x)
For instance:
log10(2 eight ) = 8∙ log10(2)
Derivative of natural logarithm
The derivative of the natural logarithm function is the reciprocal function.
When
f (ten) = ln(x)
The derivative of f(x) is:
f ' (x) = 1 / ten
Integral of natural logarithm
The integral of the natural logarithm role is given by:
When
f (x) = ln(x)
The integral of f(x) is:
∫ f (x)dx = ∫ ln(10)dx = ten ∙ (ln(ten) - 1) + C
Ln of 0
The natural logarithm of zero is undefined:
ln(0) is undefined
The limit near 0 of the natural logarithm of x, when x approaches nil, is minus infinity:
![]()
Ln of 1
The natural logarithm of one is zero:
ln(one) = 0
Ln of infinity
The limit of natural logarithm of infinity, when x approaches infinity is equal to infinity:
lim ln(10) = ∞, when x→∞
Complex logarithm
For complex number z:
z = reiθ = x + iy
The circuitous logarithm will exist (n = ...-two,-1,0,1,ii,...):
Log z = ln(r) + i(θ+2nπ) = ln(√(10 2+y 2)) + i·arctan(y/ten))
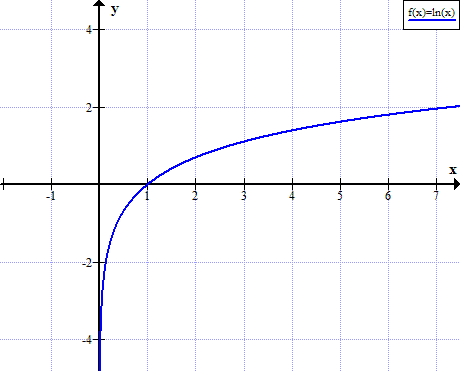
Graph of ln(x)
ln(x) is not defined for existent non positive values of x:
Natural logarithms table
| ten | ln ten |
|---|---|
| 0 | undefined |
| 0+ | - ∞ |
| 0.0001 | -9.210340 |
| 0.001 | -6.907755 |
| 0.01 | -iv.605170 |
| 0.ane | -ii.302585 |
| 1 | 0 |
| 2 | 0.693147 |
| eastward ≈ 2.7183 | i |
| 3 | 1.098612 |
| 4 | i.386294 |
| 5 | 1.609438 |
| half dozen | 1.791759 |
| 7 | 1.945910 |
| viii | two.079442 |
| 9 | 2.197225 |
| 10 | ii.302585 |
| xx | 2.995732 |
| xxx | 3.401197 |
| 40 | 3.688879 |
| l | 3.912023 |
| 60 | 4.094345 |
| seventy | 4.248495 |
| eighty | 4.382027 |
| ninety | 4.499810 |
| 100 | 4.605170 |
| 200 | 5.298317 |
| 300 | 5.703782 |
| 400 | 5.991465 |
| 500 | 6.214608 |
| 600 | 6.396930 |
| 700 | 6.551080 |
| 800 | 6.684612 |
| 900 | six.802395 |
| 1000 | half-dozen.907755 |
| 10000 | nine.210340 |
Rules of logarithm ►
See likewise
- Logarithm (log)
- Natural logarithm calculator
- Natural logarithm of zero
- Natural logarithm of one
- Natural logarithm of e
- Natural logarithm of infinity
- Natural logarithm of negative number
- Ln changed part
- ln(x) graph
- Natural logarithm table
- Logarithm calculator
- e constant
Write how to improve this folio
Source: https://www.rapidtables.com/math/algebra/Ln.html
Posted by: torrezandessaint.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Find Natural Log Of A Number"
Post a Comment